When it comes to storage devices, particularly solid-state drives (SSDs), understanding the difference between Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT) is crucial. These two partitioning schemes play a significant role in how data is organized and managed on your SSD.
Overview of MBR and GPT
What is MBR?
MBR, or Master Boot Record, is a conventional partitioning method that is commonly seen in older computers. It was launched in the early 1980s and rapidly became the industry standard for partitioned disk management. MBR uses a 32-bit partition table to hold information about the primary partitions and, if present, an extended partition. The BIOS is used to boot the operating system.What is GPT?
GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a more recent partitioning system developed to overcome MBR's limitations. GPT was included in the UEFI specification and is now commonly supported by current systems. GPT, as opposed to MBR, employs a 64-bit partition table that may accommodate a greater number of partitions and provides more sophisticated capabilities.MBR VS GPT SSD: Key differences between MBR and GPT
As two different partition scheme, MBR and GPT has many parts can be compared. So, in this part, we’ll dive into MBR vs GPT world to learn more details.Partitioning Capacity
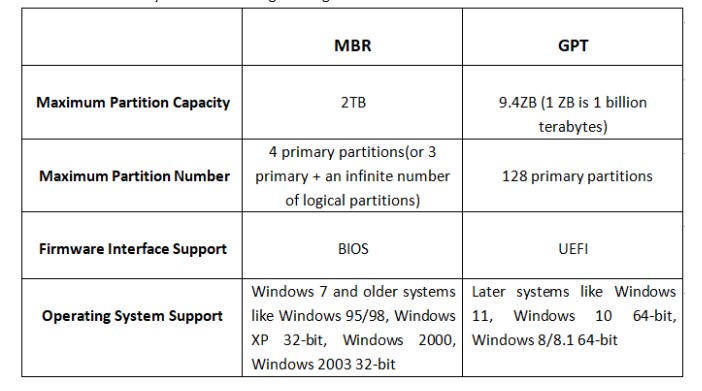
MBR supports up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition, which can be further divided into logical partitions. On the other hand, GPT supports up to 128 partitions by default, making it suitable for advanced storage configurations.Partitioning Limitations
MBR has a limitation of 2.2 terabytes (TB) for disk size, which means any drive larger than this capacity cannot be fully utilized using MBR. GPT, on the other hand, supports disk sizes up to 9.4 zettabytes (ZB), making it future-proof for even the largest storage devices.Compatibility
MBR enjoys broader compatibility with older systems and operating systems. It is compatible with both BIOS and UEFI systems. GPT, while compatible with modern systems, may face compatibility issues with older systems and operating systems that lack UEFI support.Security
GPT offers better protection against disk corruption and boot sector viruses compared to MBR. It includes a redundant backup of the partition table at the end of the disk, reducing the risk of data loss due to disk failures.Flexibility and Future-Proofing
GPT offers more flexibility and better future-proofing compared to MBR. With its larger partitioning capacity, support for larger disk sizes, and advanced features, GPT is the preferred choice for modern systems and storage configurations.Convert partition scheme between MBR and GPT in Windows
Once you acquire knowledge about MBR vs GPT, you may find it necessary to convert the current partition style from MBR to GPT or vice versa. In Windows, you can use CMD to convert disk.Press "Windows" + "R" simultaneously to lift the "Run" box. Input “diskpart” and press Enter. At the DISKPART prompt, input the following commands successively, and each command follows "Enter" pressing.
- list disk
- select disk n (where n is the disk number of target disk)
- clean (this command will erase the entire disk)
- convert gpt (or convert mbr)
- exit
Convert to GPT/MBR without data loss via professional software
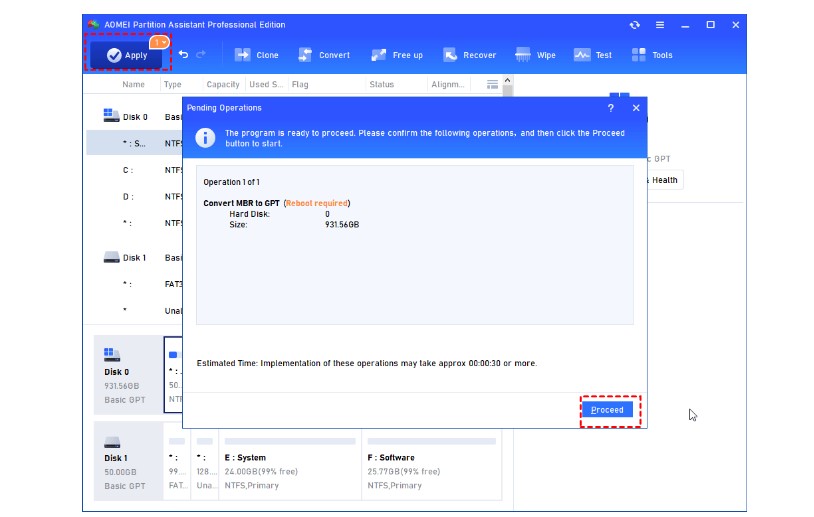
As the Windows native tools are limited to converting only empty disks to MBR or GPT, they are not suitable for users who have significant amounts of data stored on the target disk.Consequently, we would like to introduce a reliable method for converting MBR to GPT without the risk of data loss. By utilizing third-party software like AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional, a robust hard drive management tool, you can effortlessly convert between MBR and GPT on both system and data disks without having to delete any partitions. This process can be accomplished with just a few simple clicks.
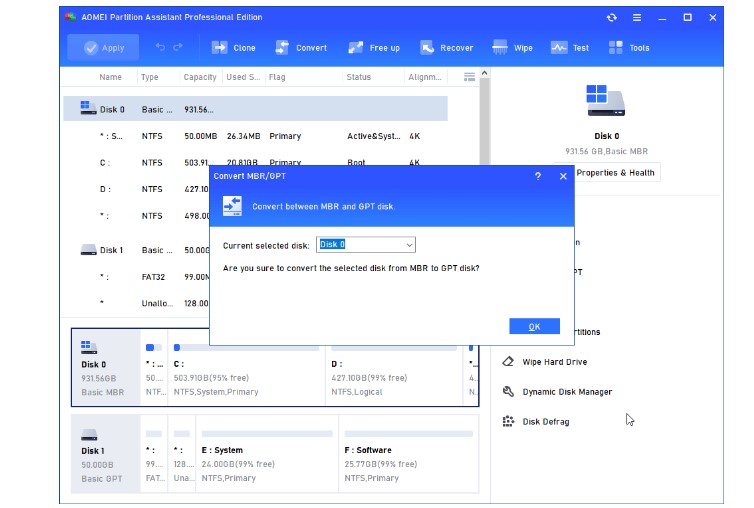
Step 1. Right-click the MBR disk that you want to convert to GPT and choose Convert to GPT.
Step 2. You'll be asked that "are you sure to convert the selected disk from MBR to GPT disk?". Click OK.
After converting a system disk from MBR to GPT, or GPT to MBR, you have to change the boot mode from UEFI to BIOS, or Legacy BIOS to UEFI for a smooth boot.
Ending
Understanding the differences between MBR and GPT is essential for making informed decisions about partitioning schemes on your SSD. While MBR is suitable for legacy systems and small drives, GPT offers superior compatibility, flexibility, and future-proofing. Assess your system's requirements, disk size, and booting capabilities to determine the most appropriate choice.To improve computer performance, AOMEI Partition Assistant can also clone disk, move installed apps, clean junk files, and so on.

No comments:
Post a Comment